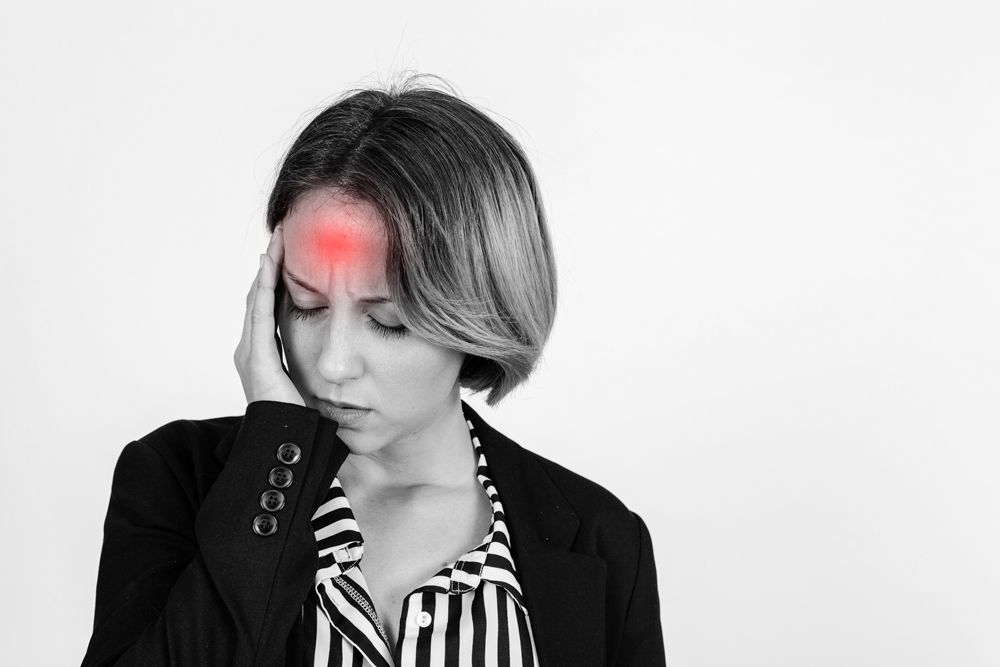
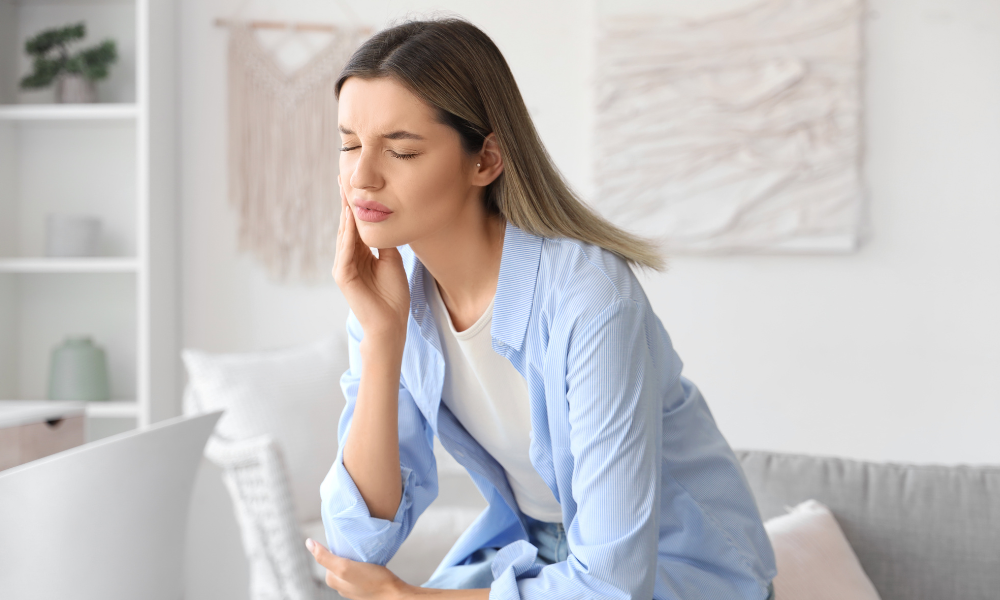
Trigeminal neuralgia, often referred to as "the suicide disease" due to the intense and incapacitating pain it can cause, is a chronic condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensations from the face to the brain. This facial pain disorder can have a profound impact on the quality of life for those who suffer from it. By understanding the complexities of trigeminal neuralgia, its symptoms, underlying causes, and innovative treatment approaches, patients can be better equipped to navigate this challenging condition and seek effective pain management strategies.
This debilitating condition is characterized by sudden, severe, and electric shock-like facial pain that can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes. The pain is often triggered by everyday activities such as talking, chewing, or even a light touch. Trigeminal neuralgia most commonly affects adults over the age of 50, although it can occur at any age. Women are more likely to develop the condition than men, and it may run in families, suggesting a possible genetic predisposition.
The exact cause of trigeminal neuralgia remains uncertain, but in many cases, it's believed to be associated with compression of the trigeminal nerve by a nearby blood vessel. Other potential causes include multiple sclerosis, nerve damage, cysts, and tumors. Due to the complex nature of this condition, it's crucial for patients to seek specialized care from healthcare professionals well- versed in the diagnosis and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia and other orofacial pain disorders, such as Dr. Bloxham atColumbia Center for Sleep Apnea and TMJ.
In this comprehensive article, we explore the intricacies of trigeminal neuralgia and its underlying causes, while highlighting cutting-edge treatment options available for patients seeking relief from this distressing condition. Read on to learn important information about trigeminal neuralgia and discover how specialized care and innovative approaches to pain management at Columbia Center for Sleep Apnea and TMJ can make a significant difference in the lives of those afflicted by this condition.
Common Symptoms of Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Facial Pain
The hallmark symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is extreme, episodic facial pain. This pain has been described as sharp, intense, and electric shock-like. Typically, the pain radiates from a specific area of the face, most commonly near the nose, eyes, or lips, and can last from several seconds to a few minutes. - Sensitivity to Triggers
Many individuals with TN experience heightened sensitivity to specific triggers. These can include normal daily activities such as eating, speaking, or brushing teeth, as well as external factors like exposure to cold air or light touch. - Pain Episodes and Patterns
TN can involve unpredictable pain episodes and patterns. The frequency and intensity of these episodes can vary significantly from one individual to another. While some individuals may go months or years without pain, others may experience daily episodes or several per day. - Anxiety and Depression
Living with the constant threat of TN pain can lead to anxiety, depression, and other emotional challenges. The uncertainty of when a painful episode might strike can be deeply distressing and affect the individual's overall mental well-being.
Treatment Options for Trigeminal Neuralgia: Medications
- Anticonvulsants
The primary line of treatment for trigeminal neuralgia involves the use of anticonvulsant medications, like carbamazepine or oxcarbazepine. These drugs help to stabilize nerve activity and minimize pain signals. - Antidepressants
Tricyclic antidepressant medications such as amitriptyline can be prescribed to individuals with TN, particularly those with the atypical form. These medications work by altering the brain's pain signaling pathways, providing pain relief. - Analgesics
Prescription-strength pain relievers can be used on a short-term basis to alleviate TN pain. However, these medications should be used cautiously due to the potential for dependency, tolerance, and adverse side effects.
Alternative Therapies: Nerve Blocks and Complementary Treatments
- Nerve Blocks
Local anesthetic injections or nerve blocks can provide temporary pain relief for individuals with TN. These injections are administered by a doctor and can numb the affected area of the face. - Complementary Treatments
Complementary treatments such as acupuncture, biofeedback, and relaxation techniques can be integrated into a pain management plan for TN. While these therapies may not replace conventional treatments, they can offer additional support and symptom relief.
Surgical and Radiological Intervention options for Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Microvascular Decompression (MVD)
MVD is a surgical procedure that aims to remove or relocate blood vessels compressing the trigeminal nerve. This procedure has a high success rate in providing significant and long-lasting pain relief for individuals with TN. - Percutaneous Procedures
Minimally invasive percutaneous procedures, such as glycerol rhizotomy, radiofrequency ablation, or balloon compression, can be used to selectively damage nerve fibers and block pain signals in TN. - Stereotactic Radiosurgery (Gamma Knife)
Stereotactic radiosurgery, also known as gamma knife treatment, involves the use of focused beams of radiation to target the trigeminal nerve. This non-invasive procedure can provide pain relief by damaging the nerve and interrupting pain signals.
Conclusion
Trigeminal neuralgia is a complex and debilitating orofacial pain disorder that can profoundly impact an individual's life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential for individuals struggling with this condition. Dr. Bloxham at Columbia Center for Sleep Apnea and TMJ is dedicated to diagnosing, treating, and managing trigeminal neuralgia and other orofacial pain disorders. With the right approach and a multidisciplinary treatment plan, individuals can regain control over their lives and experience a significant reduction in pain and discomfort. Contact us now to speak with our TMJ pain doctor.